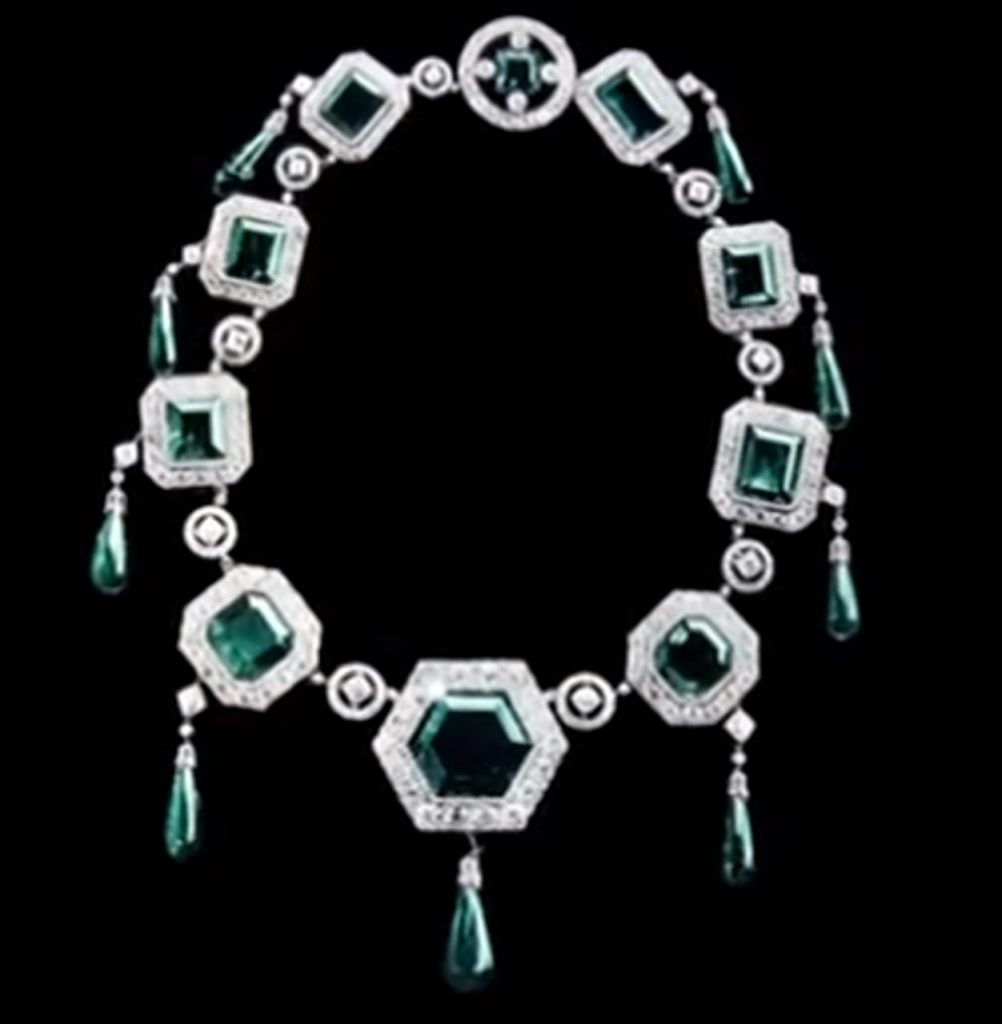
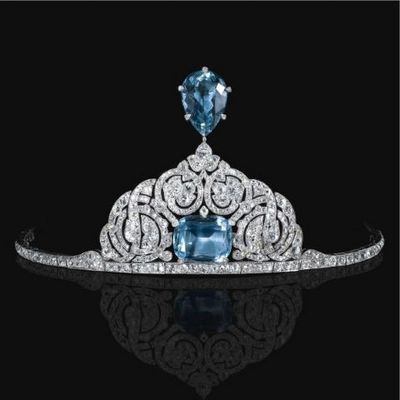
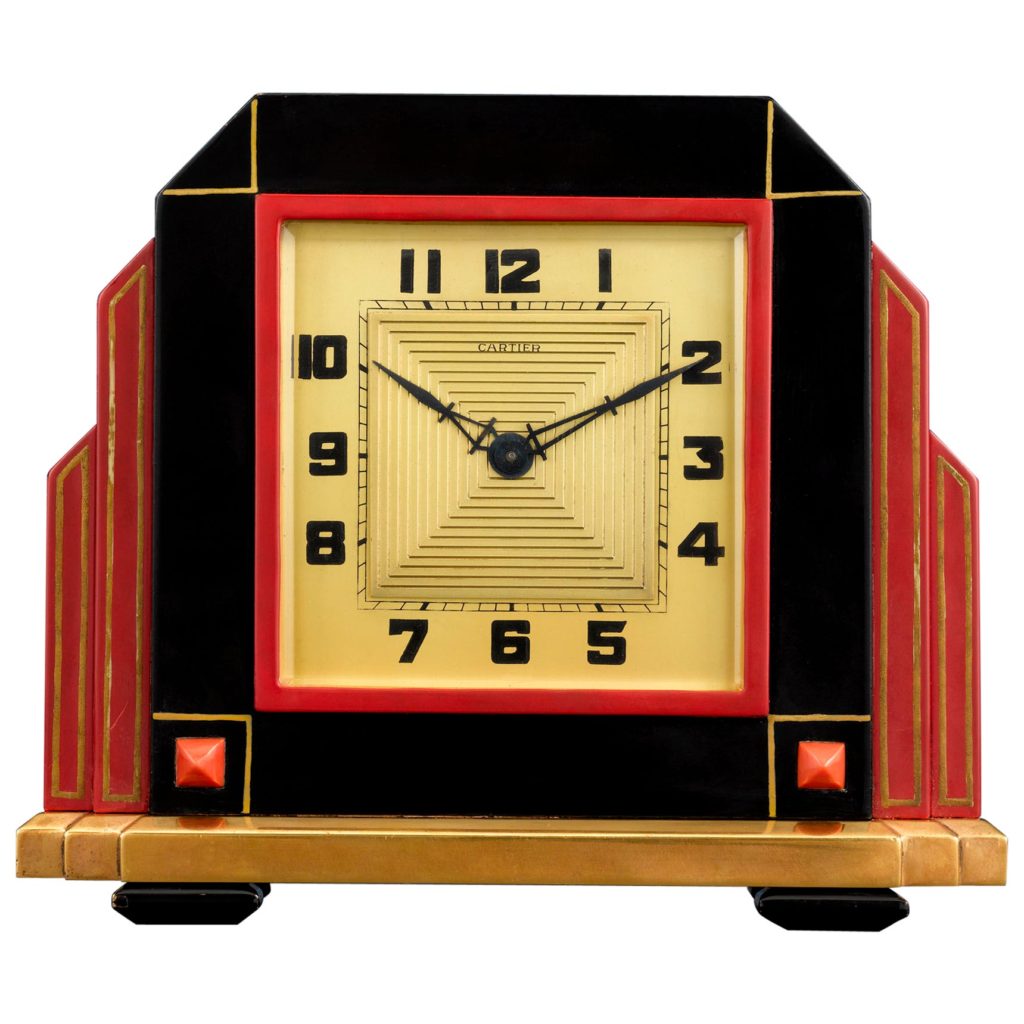
“The Cartiers: The Untold Story of a Jewellery Dynasty” by Francesca Cartier Brickell

The Cartiers: The Untold Story of a Jewellery Dynasty by Francesca Cartier Brickell is a family history penned by the great-great-great granddaughter of the iconic jewellery firm’s founder. The Cartiers took Francesca more than a decade of research. It all began when the family gathered to celebrate her grandfather’s ninetieth birthday. Over the years he would often refer to a pile of family correspondence that seemed to have gone missing. At his ninetieth birthday celebrations Francesca went to the cellar to locate the bottle of wine he sought and to her joy stumbled upon a chest. She pried it open to discover it stuffed with letters. She decided to chronicle the family as her grandfather was the last who had actually worked in one of the firm’s branches before it was sold in 1974. She was working as a financial analyst covering the retail sector and raising a young family in London which meant that Francesca had to travel every weekend to south France to be with her grandfather to record his accounts. The result is this fascinating chronicle of a remarkable family that through its determined ambition to rise through the socio-economic ranks of French society got exactly what they wanted. From an impoverished background in the early nineteenth century to being welcomed in the courts of many prominent royal families across the world and counting amongst their clients professionals such as bankers, actors, musicians, politicians etc. Astonishingly this ambition and drive was evident across generations. With a steely determination the family knew what they desired — luxury retail, upmarket clientele, elegant and diverse product range and ensconced in the middle class. The family was clear that they had to remain clear of debt, they had to innovate and be creative and not necessarily always look at their competitors but look around for inspiration and ideas.

While every generation of the Cartiers had contributed constructively to the establishment of the family as a name to contend with in the jewellery business, it was the fourth generation of three brothers — Louis-Joseph, Pierre Camille and Jacques-Thoedule ( the author’s great-grandfather), who truly made the jewellery firm a name to reckon with. A name that is recognised decades later. Designs created by them continue to be recognised and attract astronomical prices at auctions as evident in the Maharajas & Mughal Magnificence — spanning five centuries — auction organised by Christies, June 2019. Museum quality jewels belonging to Sheikh Hamad Al Thani with 388 lots were up for sale. Another equally successful and prominent white glove sale, consisting predominantly of Cartier designed jewellery, was the sale of the Duchess of Windsor’s jewellery in 2010.
…there were twenty-one Cartier pieces in the sale. Eight of them reached over one million dollars. One exceeded ten million dollars. In total, the number of Cartier lots accounted for just 5 percent of the overall number but ended up contributing a quarter of the final $109 million value.
“Cartier” is synonymous with luxury, fine living and power. The jewellery designed by the firm drips with elegance, power and money. It is meant for the rich. The Cartier gemstones belong to the privileged sections of society. But that does not prevent millions of others from appreciating fine craftsmanship, the stunning arrangement of gem stones especially diamonds, and the play of colours as in the Tutti-Frutti range. The benchmark set by the Cartiers for quality of work, excellence, discretion in dealing with clientele and managing the brand globally is astounding as it spans a couple of centuries. Their hallmark is to create stunning designs that wow their customers for their uniqueness. This is primarily due to the Cartier family’s keeness to experiment and look for inspiration elsewhere rather than at their competitors. These decisions helped create an iconic brand whose designs astound the world decades later. A testament to this fact have been the aforementioned auctions of December 2010 and June 2019 where the Cartier jewels were the key attraction.
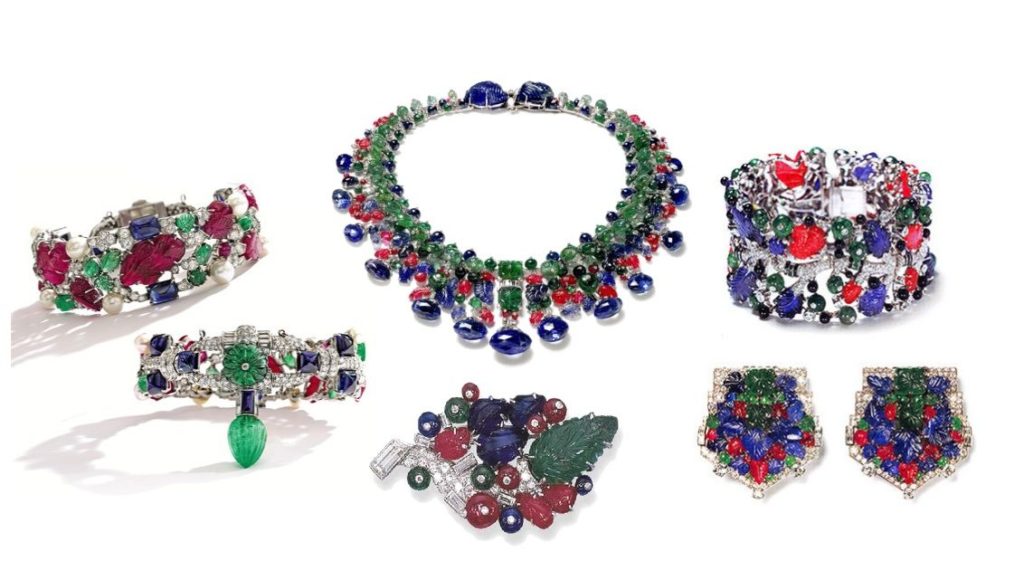

The Cartiers were responsible for many innovations in their jewellery designs, many of which were a response to the times, but have withstood the test of time. For instance, the Tank watch. Louise Cartier created this watch for pilot Santos-Dumont inspired by the Renault FT-17 light tank, a mechanical hero of the Great War. Santos and Cartier were friends. Santos was an avid pilot who had begun to find it difficult to extricate his pocket watch from his clothes to check the time while in flight. He mentioned this in passing to Louise Cartier who took it on as a challenge to design something that would be convenient to wear, consult without compromising on its elegance. So far wrist watches had been designed for women with the emphasis more on the jewellery designed rather than the watch itself. So the perception in most people’s minds was that it was a feminine accessory. Louis Cartier designed an elegant unisex wrist watch where the only concession to it being designed by a jeweller was the plain sapphire winder on the right-hand side. The simple, functional, elegant lines of the Tank watch made it iconic from the word go, not least because Santos flaunted it everywhere he went. Given that Santos was a style guru of his times, Louis Cartier could not have wished for a better launch pad for a new product. Although an entire range of Cartier Santos wrist watches was released only after some years. Much later Andy Warhol owned one but not for its intended purpose. “I don’t wear a Tank to tell the time,” said the man who invented the concept of 15 minutes of fame. “In fact, I never wind it. I wear a Tank because it’s the watch to wear.” Platinum versions of some of the earliest versions of the watch are collector’s items. Here is a lovely 2017 Forbes article celebrating the Tank watch’s centenary.
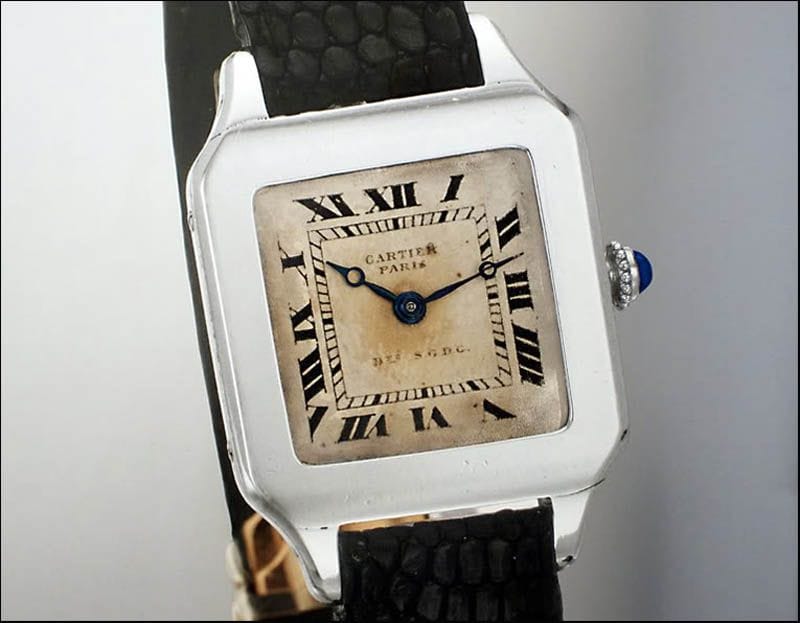

The first Tank watch designed by Louis Cartier for Santos-Dumont 
Rudolf Valentino insisted on wearing his Tank watch in the film”Son of the Sheik” (1928). This was the first appearance of the Tank watch on screen.
Product diversification was a key to Cartier’s success. The family was keen to capitalise on fashionable trends while keeping an eye on marketable commodities without compromising on style, elegance and being recognised as a luxury brand. In order to create new designs and become the leading tastemakers in the market, the three Cartier brothers — Louis, Pierre and Jacques — began to search for alternatives. While the Tank watch is a great example of seeking inspiration from key industrial products of the age; there were other such experiments too. Such as the Cartiers were the first ones to introduce the use of platinum for setting gemstones. Fairly early on they had discovered that the metal is the most ductile of pure metals but less malleable than gold, so a perfect choice to make fine jewellery. The inspiration for using this metal came from their observation of rail carriages where the metal was often employed. It was imperative to focus on creating a range of products for various reasons. Such as the onset of war and affordability of new designs, a surge in demand to remount heritage pieces of jewellery in more modern styles, using bejewelled accessories for different social occasions and not necessarily always extravagantly set pieces. ( Here is an article on the Cartier exhibition of 2018 which showcased more than 300 pieces, many on loan from royal families and private collections.)
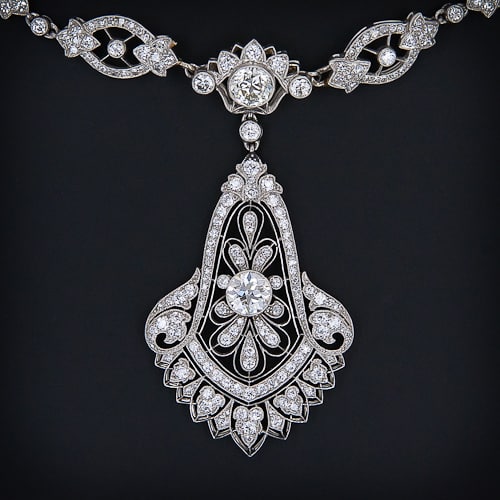
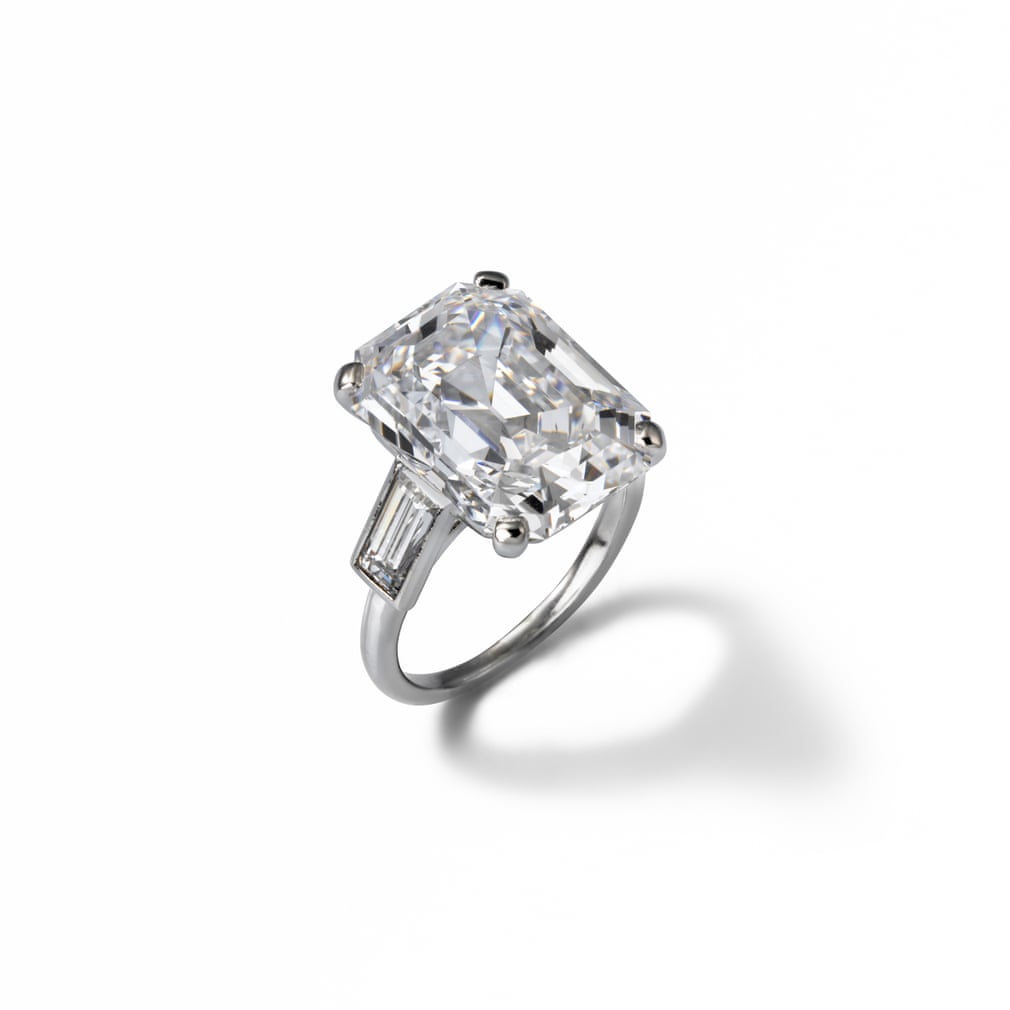


Using platinum in their designs enabled the Cartier brothers to experiment with fine jewellery. They created tiaras, rings, fabulous necklaces, brooches, hair pins etc. This was a brand new idea in jewellery design. So much so that when they began using it to set gem stones, this unusual use of the metal had not as yet been recognised in this manner ensuring that it did not attract any tax and helped reduce the cost of jewellery being created.
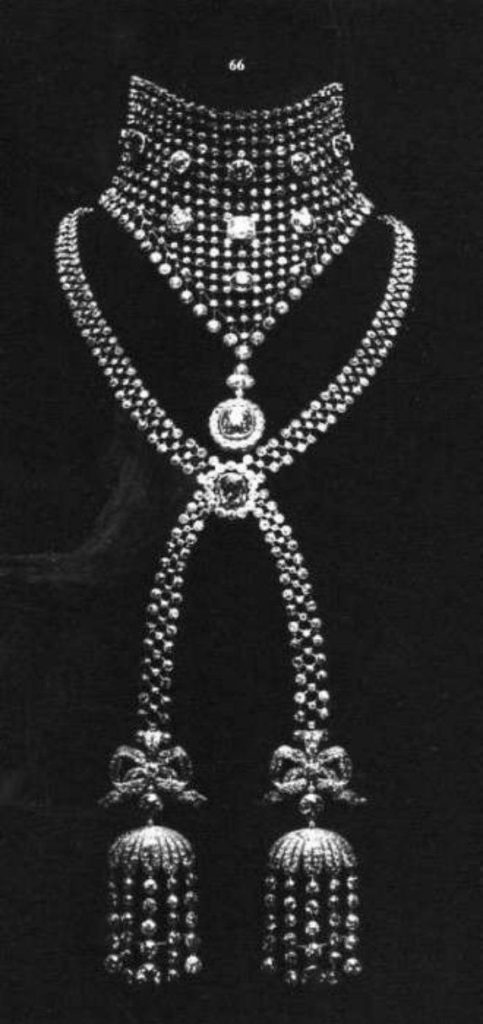


The versatility of the metal helped the wildly imaginative Louis Cartier to sketch extraordinary designs, using a range of gem stones, to create opulent pieces of jewellery, raising the bling factor by many degrees. He also was deeply influenced by the Art Deco movement. He was ably assisted in fulfiling his dreams of creating iconic pieces of jewellery when he hired Charles Jacqueau.While out taking a stroll Louis Cartier had spotted an exceptionally beautiful balcony being installed. Impressed by its avant-garde geometric style and sense of proportion, Louis spotted the young designer on a ladder supervising its installation. He immediately requested Charles Jacqueau to come for an interview to his firm but Louis Cartier’s offer was firmly rejected by the young man as he was already committed to projects. Once done, Jacqueau visited Louis Cartier who set him a test of designing jewellery with three piles of gems — rubies, sapphires and diamonds. Jacqueau excelled in the text. Cartier was delighted his instinct had proved correct and offered the young man a job on the spot. Jacqueau had trained at Paris’s famous art school, the École des Arts Décoratifs. His professional expertise was in large metal structures, not in tiny gems. But he accepted the assignment at Cartiers as he was intrigued by this new type of work.


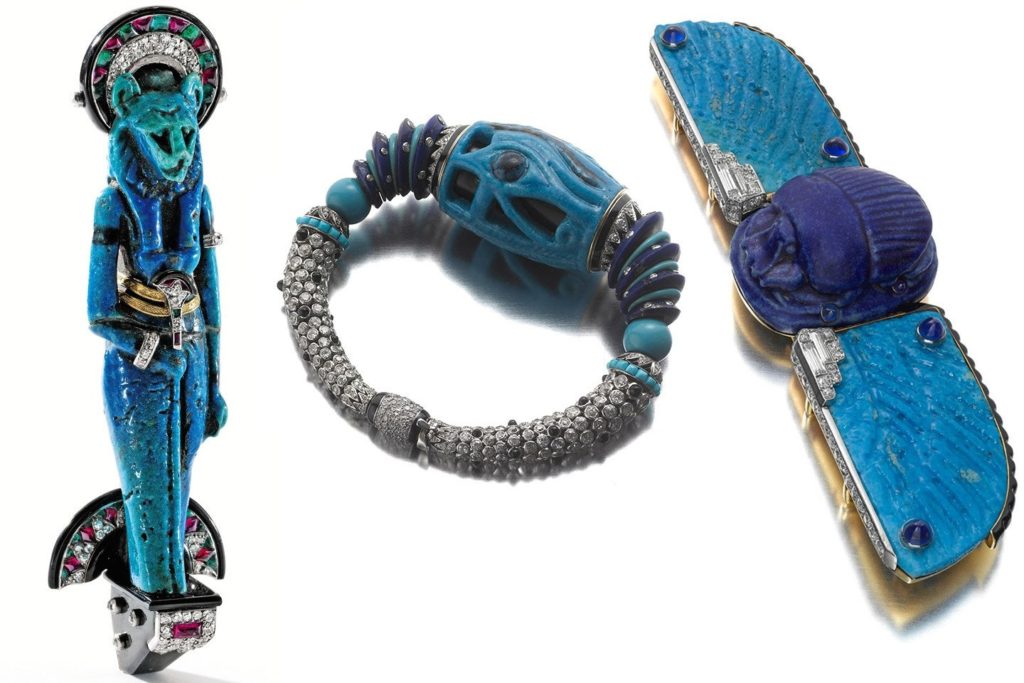
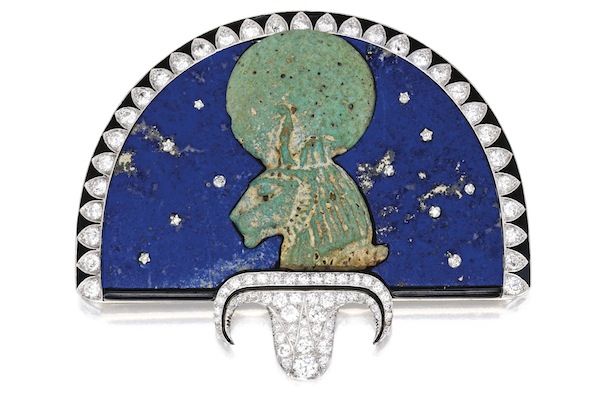
It suited both employer and employee to be creatively energised for these were exciting times to be in Paris. The Art Deco movement was in vogue. Also in news were fascinating archaeological expeditions such as Howard Carter and Lord Carnarvon’s of 1923 where they discovered King Tutankhamen’s tomb. The Cartier brothers were inspired to create a new range. They would scour antique shops for remnants of ancient Egyptian art. Some dating hundreds of years back. Then these would be incorporated in new settings while being mindful of the original beauty of the Egyptian art. Simple but classic style statements were created such as hair clips, belt buckles, bracelets, brooches etc. Art Deco Egyptian revival jewellery was soon the rage. Today these creations are collector’s items as few were sold and remain in private collections, very rarely are they made available for auction. Many others remain in the Cartier collection. According to a 2015 Vanity Fair article:
… almost a century later, this refined mash-up, known as art deco Egyptian Revival jewelry, is among the most unique, and most highly-coveted in the modern market—and is priced to match. Many are considered masterpieces of the jewelry canon, but few land beneath the glass at the Met or even smaller museums. Instead, Egyptian Revival pieces are often purchased by private collectors with massive budgets and highly developed tastes.
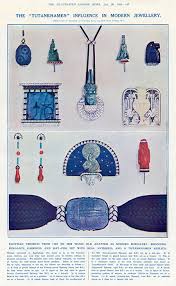


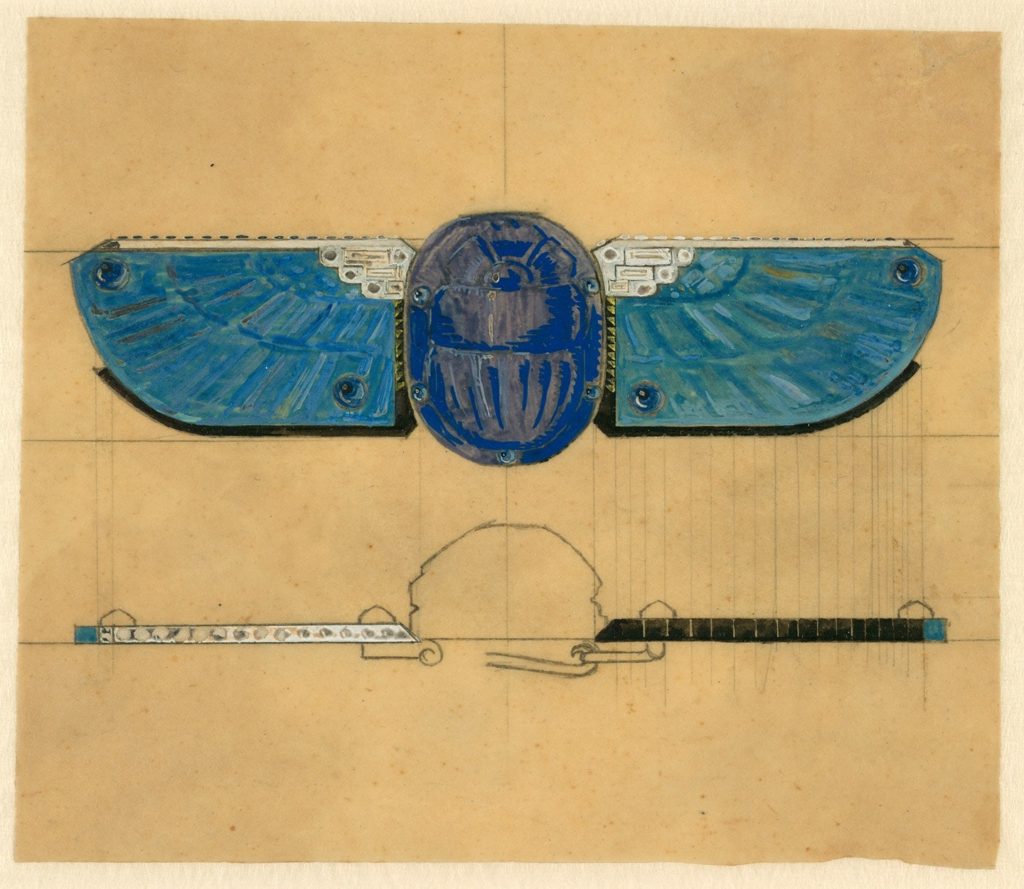
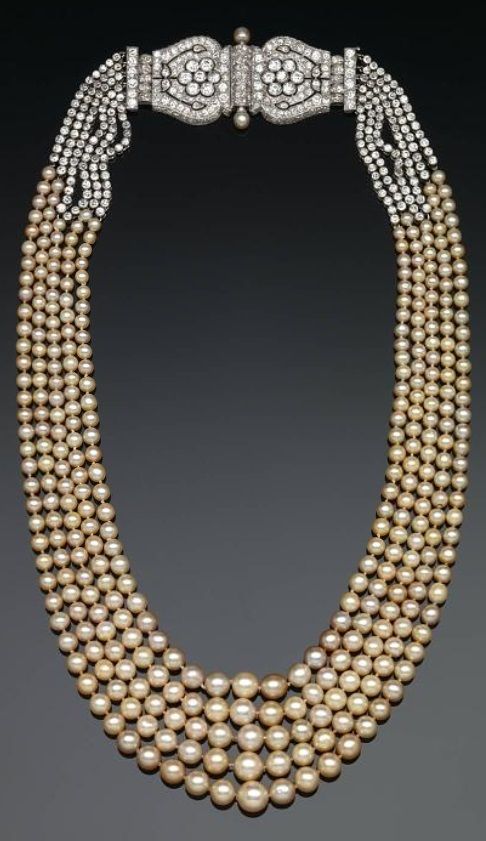
Another innovative introduction in contemporary jewellery design was to make the pearl string an attractively elegant accessory. Most often than not the Cartiers excelled in using natural pearls, exquisitely graded and strung so beautifully. From a single strand to multiple strings on one necklace became a fasion statement that has once again survived decades of stylish dressing. Jackie Kennedy Onassis was known for her pearl strings. Equally well-known were the more extravagantly strung 10-string creation made for the Maharajah of Patiala.
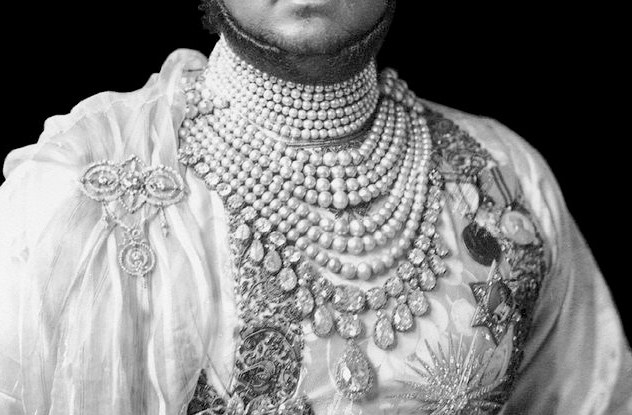


The Cartiers had a long and lucrative association with some of the notable royal families around the world. Some of their best clients were the Romanov dynasty before and after the Russian Revolution of 1917 and many of the Indian royal families. The Russian market was not easy to cultivate but once done the Cartiers were steadily commissioned to create new pieces of jewellery. Even after the collapse of the dynasty, many of the Russian nobles who fled the country, made their way to Europe clutching bags of jewels. These were then either sold as is or some pieces were remounted in new designs by jewellers such as the Cartiers. A classic example being the Romanov emeralds worn by the Grand Duchess Vladimir and later acquired by Edith McCormack Rockefeller and Barbara Hutton — in that order. Each time the deal was brokered by Cartier and the gems remounted as per the wishes of the client.
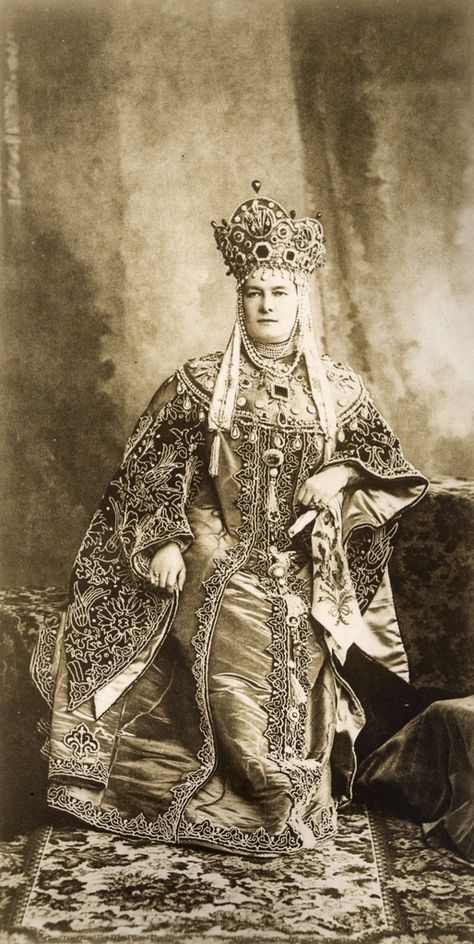
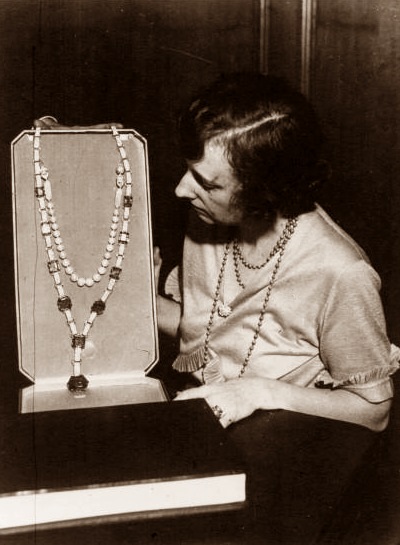
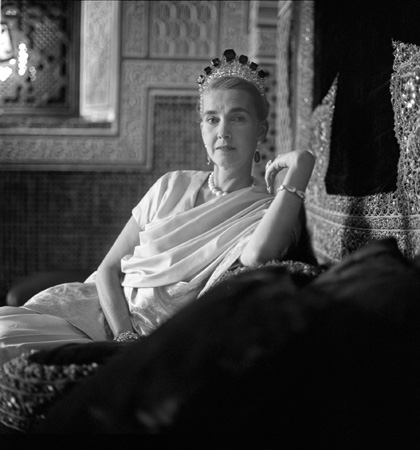



Their association with the Indian royal families influenced the Cartier range of jewellery too. It brought in a profusion of colours which was unheard of in European fashion circles. A burst of colours on a string or a bracelet much akin to Indian kitsch looked good when used with brightly coloured real gems such as sapphires, rubies and emeralds. This range began to be called Tutti-Frutti or the cringeworthy term “Hindou” jewellery, coined by Jacques Cartier. “Tutti-Frutti” as a description of the jewels began to be used only in 1970 despite the first pieces of jewellery being commisioned by Queen Alexandra in 1901 to match three of her Indian gowns.


The Cartiers: The Untold Story of a Jewellery Dynasty by Francesca Cartier Brickell is an absorbing account of a family that really carved a niche for itself. The family name became a strong brand unto itself. The generations of men in control of the firm were innovative and creative ensuring that their pathbreaking designs wowed contemporaries but have also withstood the test of time and continue to attract astonishing prices. What is truly mesmerising to read is how every single generation was very focused, determined and ambitious to develop the brand and in order to do so they recognised the need to be prudent in their business plans. For instance when their local partner in Russia was insistent that they set up a standalone store, the Cartiers refused recognising that the investment costs outweighed the profitability of such a venture. Similarly when a brother travelled to the Indian subcontinent to source gems and sell some of their recent creations, the other brothers wanted to be kept abreast of all details, with a keen eye on the profit margins made. Much of these conversations are detailed in the correspondence discovered in the trunk found in the cellar. All these tiny dots in the family’s past are connected well in the able hands of Francesca Cartier Brickell who in all likelihood has brought in her professional expertise as a retail sector financial analyst to understand the Cartiers. It certainly shows in the competent arrangement of the narrative.
The layout of the book is interesting. Peppered throughout the book are boxed extracts from the conversations Francesca had with her grandfather. They help in not only breaking up the monotony of the text-heavy book but also make much of the history “accessible” for these snippets of testimonies by a gentleman who witnessed many of the events documents. Or he recalled family anecdotes that supported many of the facts Francesca unearthed during the course of her research.
Curiously though Francesca Cartier Brickell while being intent on keeping her family’s image intact is unable to bring a modern distancing from the facts shared. While it is understandable that the Russians were amongst the best clients the Cartiers had but to be dismissive of the assassination of “the prime minister ( and Cartier’s good client), Pyotr Stolypin” by a “leftist revolutionary” is just one of many examples in the book where a more nuanced understanding of the socio-historical events in this family history would have been welcome. Another example is consistently referring to the “Hindou” jewellery despite it being factually incorrect as not all the Indian royals were Hindus apart from which it is an uncomfortable term in present times; a simple recognition of which would have been a gracious gesture. While these are tiny editorial details that perhaps were in the author’s control there are some other elements in the book production that do not seem to have been in her purview. It is almost as if many corners were cut to keep the price point of the book “affordable” than take into account the history of an iconic luxury brand which demanded to be heavily illustrated as well. There are innumerable photographs throughout the book. Most of them are in black and white. Unfortunately most of them are shoddy reproductions making it impossible to discern the beauty of the jewellery. For instance on p. 360 there is an image of a group of women wearing tiaras but it impossible to appreciate the beauty of the jeweller’s craftsmanship. There are many examples such as this in the book. Even the two sections of tipped in colour plates are frustrating to read as the provenance of the jewels is not mentioned except in fine print towards the end of the book; making it extremely difficult to consult. Or there are many situations where the text refers to a piece of jewellery but is not pictorially referenced in the text. This makes reading the book a very slow and laborious process for one has to constantly search the Internet to search for references to the jewels mentioned. Perhaps it is symptomatic of the new age of reading — a blend of the print and digital experiences but it is also tantamount to lazy book production by compromising on the quality of such a potentially fine book. It is upsetting too since this is an account of a family that is synonymous with elegance and sophistication but the book production does the Cartiers a disservice for its clumsiness. A tiny detail such as a red silk ribbon inserted as a bookmark custom monogrammed with the Cartier signature would have added a subtly elegant detail.

Be that as it may, except for these tiny hiccups, The Cartiers is an absorbing read. Many will enjoy reading it. There is much to be learned from it.
11 March 2020








